 Armando Caligiuri electrons in
motion
Armando Caligiuri electrons in
motion

Welcome to the page dedicated to InformationTecnology
In this page I will try to define with suitable
words the immense world behind the word "InformationTecnology",
as you can understand it is not an easy task, but I will try also in
this case. Of course it is impossible to condense a very vast subject in
this small text, but if you intend to deepen or need professional advice
(given my experience in the field that began when I was a child, that
is, since 1979) you can contact me via the "Contacts"
page.
In this page we will deal with the definition of computer science and the hardware of computer systems, for software and computer networks I have prepared separate pages that you can reach by clicking on the links in the line above or at the bottom of this document.
Information technology is the science that deals with processing and processing data, information, physical quantities and services in an automated way, to do so it operates with electronic systems (computer systems) formed by billions of logic gates, which need signals to work digital or numeric, that is, which have only two states, state 0 or off, and state 1 or on, naturally to acquire and process analogue signals (see "electronics" page), it is necessary to previously convert them into numeric (or digital) by means of an A / D type converter that is from analog to digital. The converter transforms the signals with continuous variation of amplitude and frequency into a sequence of logic zero and one digital equivalent to the input signal. At the end of the processing, the digital signals can be reconverted into analogue if necessary by means of D / A converters, i.e. from digital to analogue, which perform the reverse operation, i.e. transform a sequence of zero and one logic states (or on-off, or maximum voltage-minimum voltage) in an analog signal (value between 0 and infinity) corresponding to the digital sequence, for further information on the converters you can contact me via the "contacts" page.
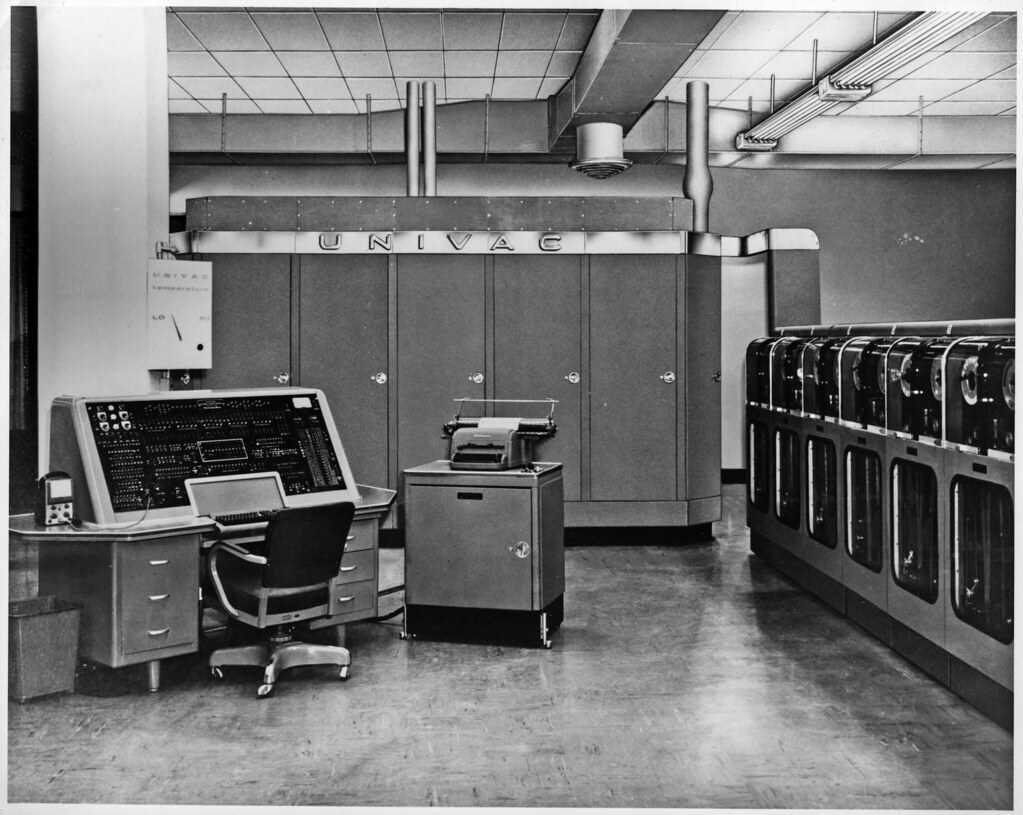
Management room of the first commercial computer, the UNIVAC 1 IT system of a well-known American company
TheInformation
technology and computer systems have evolved above all
in the field of telecommunications and information, where it has almost
completely supplanted traditional systems thanks to the possibility of
data processing, the high immunity to disturbances of digital signals
and the progress of electronics in the miniaturization of circuits and
in the containment of system manufacturing costs.
The progress of
electronic circuits has therefore made it possible to bring
information technology out of a strictly professional environment, and
to bring the PC into every home and office like a household appliance.
or personal computer, which has made the digital world
with its universe of information and opportunities available to anyone,
recently the appearance on the market of battery-powered and
touch-sensitive screen devices such as smartphones and tablets,
has expanded the range of opportunities available, allowing at the same
time external portability and therefore continuous usability.
Personal computer complete with peripherals Portable personal computer, known as Notebook
Latest generation smartphone Latest generation tablet
Computer systems are made up of two inseparable elements, hardware and software.
The hardware (translation from English, hard, concrete) is identifiable in the logical electronic circuits that we find inside the PCs of smartphones or tablets, the keyboard, mouse and monitor are part of the hardware.
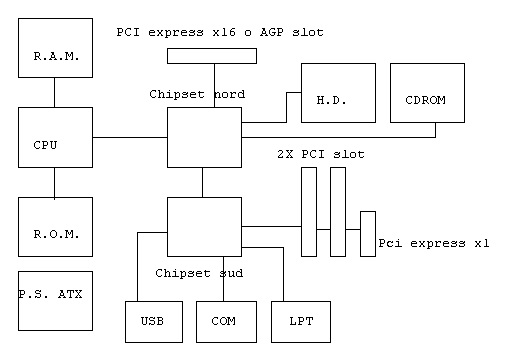
As previously mentioned, information technology makes use of electronic systems for its operation, as in the case of the PC, which is the computer system that concerns us most closely, and from which all the other data processing systems have also taken inspiration. and use of the contents. The circuitry has now become standardized and can be represented in a very simplified way with the block diagram shown in the figure.
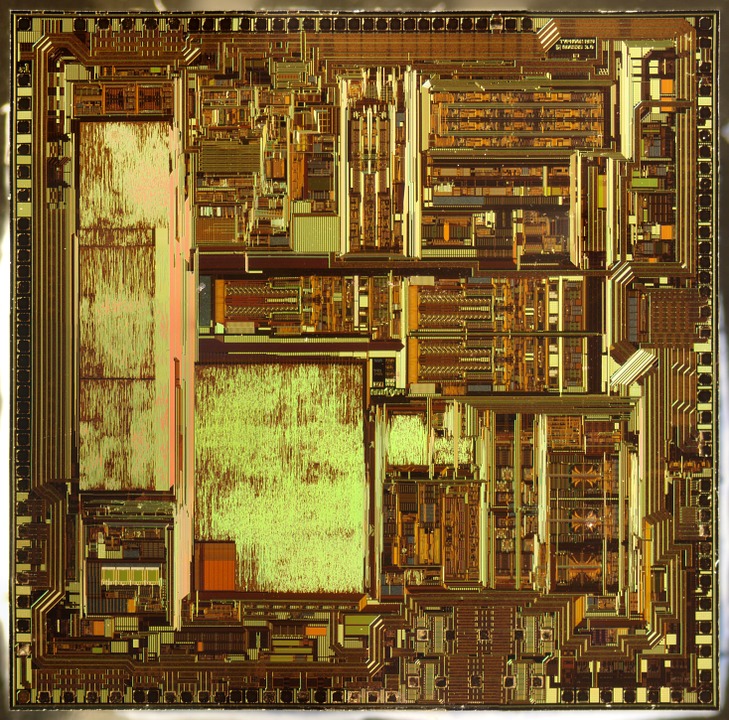
The C.P.U. (central processing unit) is the component commonly called microprocessor, it represents the heart of the PC, in it data is processed in the form of sequences (strings) of digital signals, it is a very complex integrated circuit LSI (large scale integration) formed by millions of Transistors and MOSFETs, few have the know-how to build such a component, currently there are only two left in the world who have the resources to develop CPUs for PCs at high levels.
The CPU uses other components to function, they are:
The R.A.M. (random access memory), is connected directly to the CPU, guarantees fast access and is used to process data in real time. It is a volatile memory and its content is lost as it is continuously erased and rewritten during its operation, the quantity and quality of the RAM to be installed depends on the complexity of the data to be processed, as a general rule it is installed as much as possible compatibly with system costs and energy consumption.
The R.O.M. (read only memory) is a read only memory, connected directly to the CPU, which is not involved in the digital data processing process but serves as a genetic kit for the PC. It contains the hardware configuration data, it contains the BIOS and the CMOS and you cannot change the content (in theory no, in practice yes).
The north and south chipsets are large LSI integrated circuits, they are the nodes of intermediary between the CPU, the data storage devices and the outside world, in fact they are connected to the USB ports (universal serial bus) to which we can now connect everything, the COM (serial port) and the LPT (parallel port), the burner-cd-dvd player and the hard disk (hard disk) are connected to the north chipset, and can also contain the video conversion unit integrated inside them (video card) and audio processing unit (sound card).
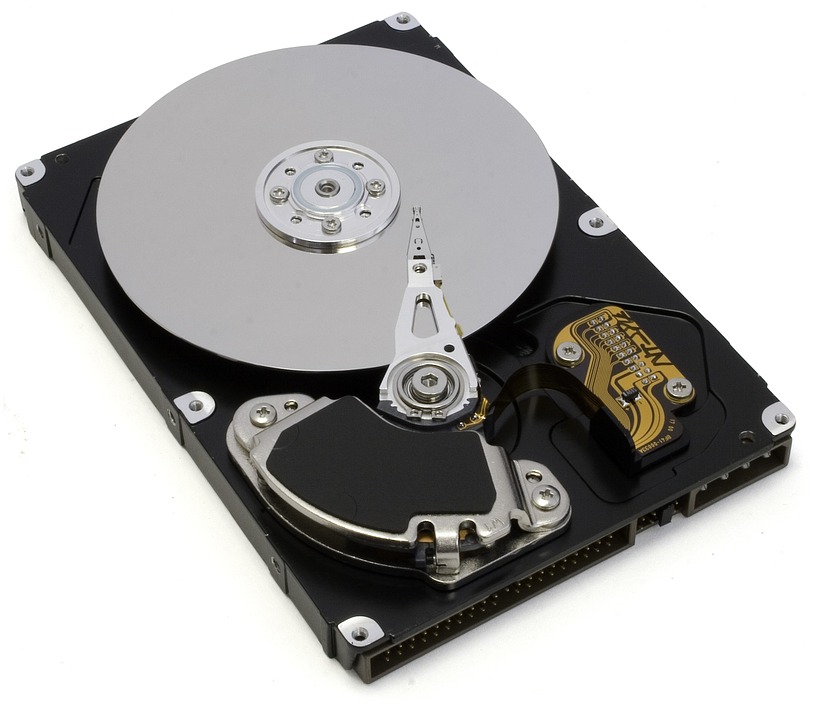
The hard disk is a complex and delicate electromechanical component, it is formed by various platters kept in rotation at high and constant speed by a precision electric motor, a magnetizable substance is deposited on the surface of the platters, and a head that runs continuously on of them it writes a sequence of 0 (demagnetized substance) and 1 (magnetized substance) corresponding to the data to be memorized and preserved. For some time, solid state hard disks (SSD) have been created, which are built using FLASH type memories, writable for a certain number of cycles, usually high, they are becoming increasingly popular because they allow reading speeds (not writing) higher than traditional electromechanical disks, but their cost is high compared to traditional electromechanical hard disks and reliability suffers from the limitations of solid state memory technology, essentially you may find yourself in the situation of having lost your data at any moment if the memory locks up and refuses to respond, this could happen after long memory write cycles. However, even in the case of SSDs the evolution runs fast and the reliability of today's systems has become very high, the problem of the cost per Gb still remains, which is at least double compared to traditional hard disks.
The PC also has a certain number of ports inside (slot or comb connector) that allow expandability, i.e. the possibility of adding cards that can perform particular functions and therefore make the computer system suitable for specific uses.
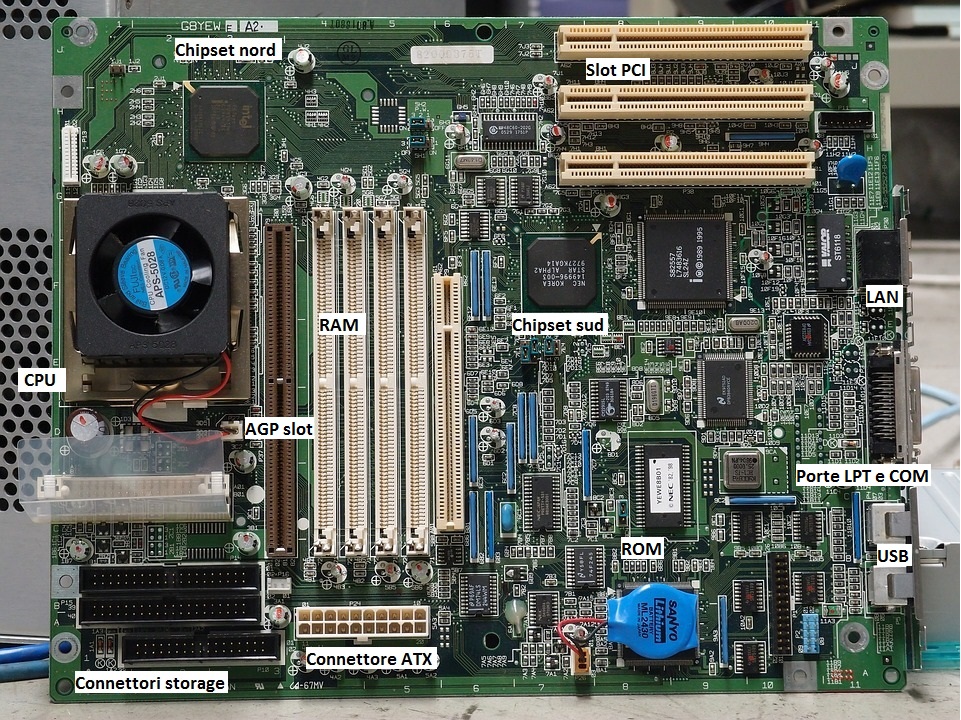
Many of the components just mentioned are housed on a main electronic board called motherboard or mainboard, it houses almost all the electronic circuitry represented in the block diagram that you can find a few lines higher, in addition to the voltage stabilizers for the cpu and the RAM and at the interfacing ports with the outside world.
Everything is powered by an apparatus (ATX power supply) that supplies the various voltages necessary for the operation of the CPU and the components it needs, it must be of good quality and must keep the voltages stable and clean, the necessary values are usually 3 , 3V, 5V, 12V, -12V, -5V, with currents of the order of 25A for 12V and 3.3V.
Other devices called peripherals
are connected to the actual PC via the ports connected to the chipset,
they are electronic hardware devices that allow you to give commands to
the PC (input peripherals) or equipment that use the
processed data (output peripherals).
Other input devices are the Mouse
the keyboard and the
scanner, on the other hand the
monitor and the
printer are output devices.
Here are some zoomable images, which will allow you to understand what
we have said so far.
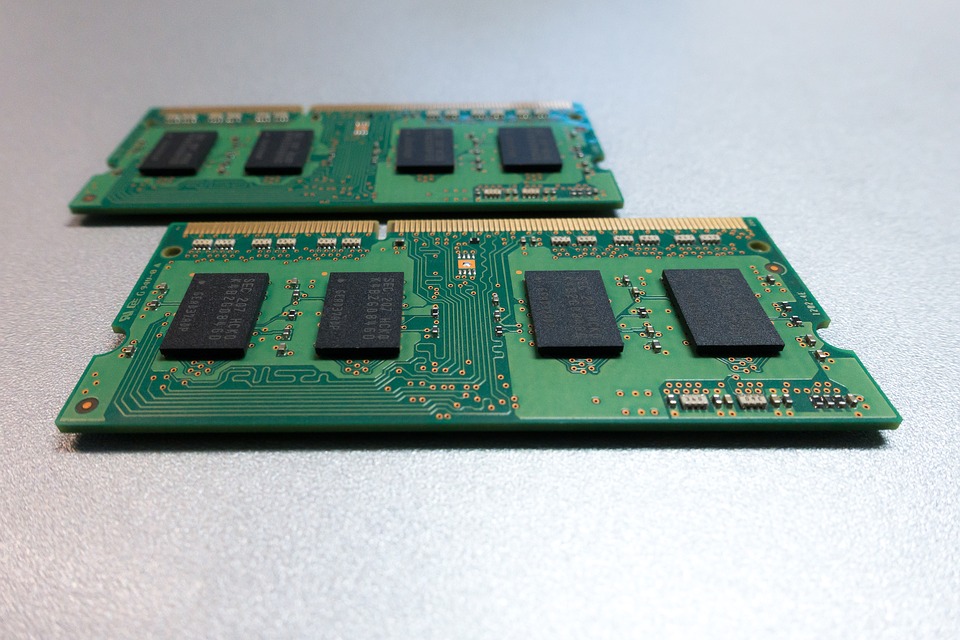
Outdated and current data storage components SODIMM DDR step 3 RAM modules
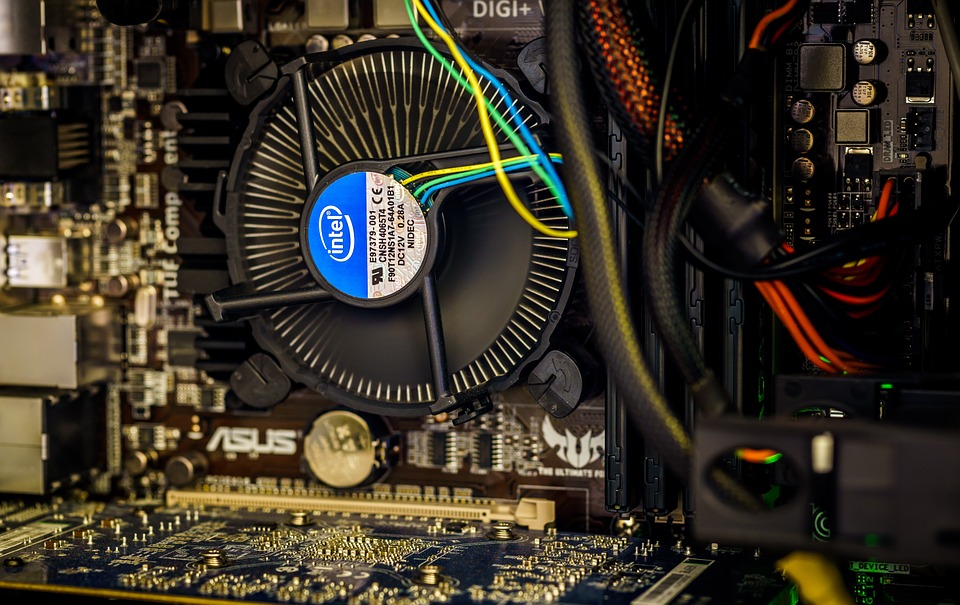
Cpu mounted on mainboard with its heatsink CPU seen inside with the microscope
Mainboard with component identification Hard disk without cover seen inside
The software or application (app), on the other hand, is the information or digital content that we must process or use (process through the hardware), which can be stored (stored) in a hard disk or in a USB memory or other computer medium . The operating systems, drivers and word processing suites are part of the software, which we will discuss on a separate page.
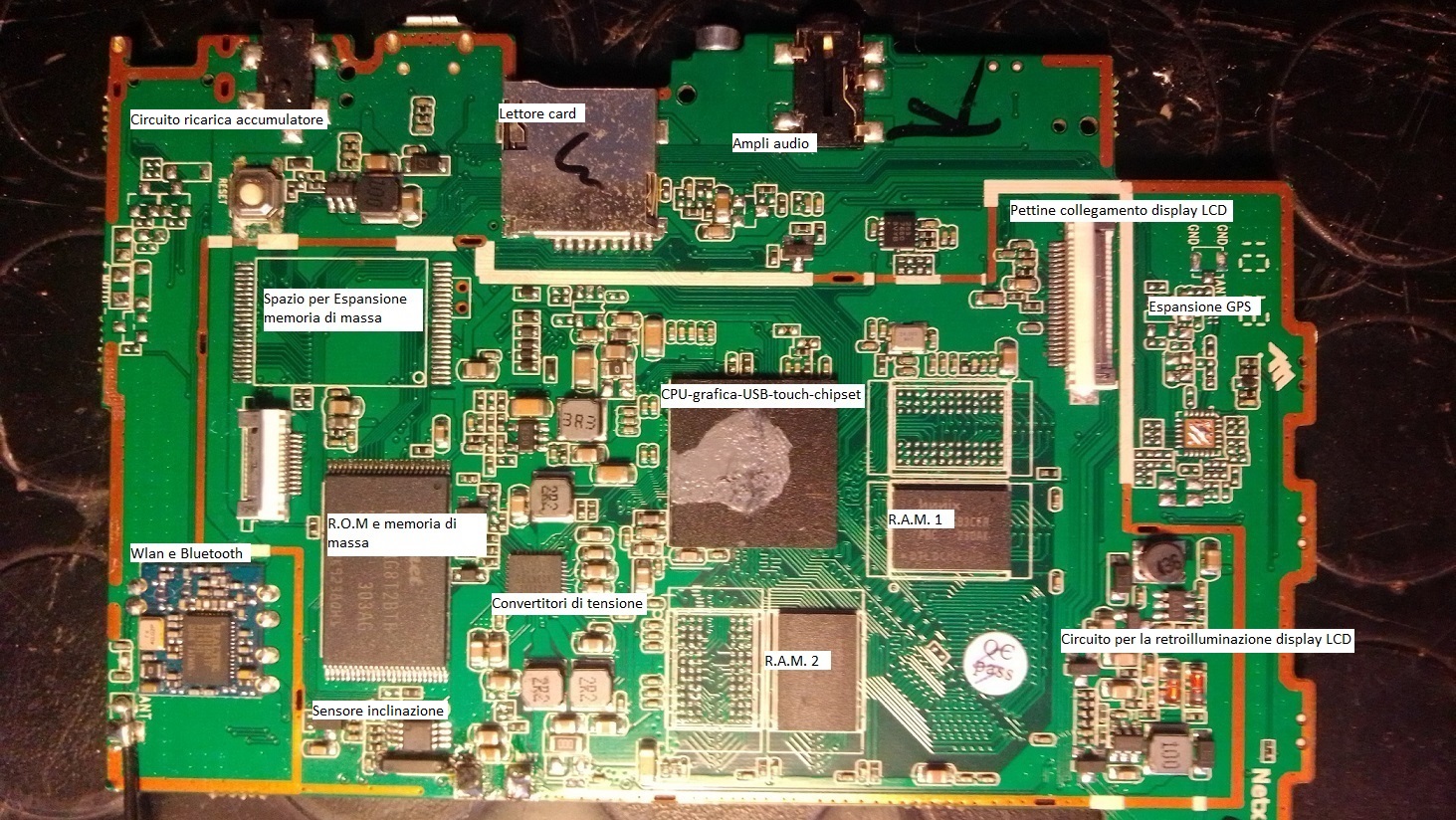
The digital architecture of the P.C. thanks to its adaptability and versatility it has now become standard for almost all electronic equipment, new generation LCD televisions, DAB radios, tablets, smartphones and in general all equipment that has a C.P.U. provide even if in a small way an operation such as that of the PC, if you need to process an analog signal it is converted into digital, this is because the digital PC clone architecture can take advantage of all the advantages connected to it, such as the pushed miniaturization of integrated circuits and electronic components, large-scale production with consequent reduction of production costs and an easy and smart approach due to the programmed logic in place of the wired logic used up to now.
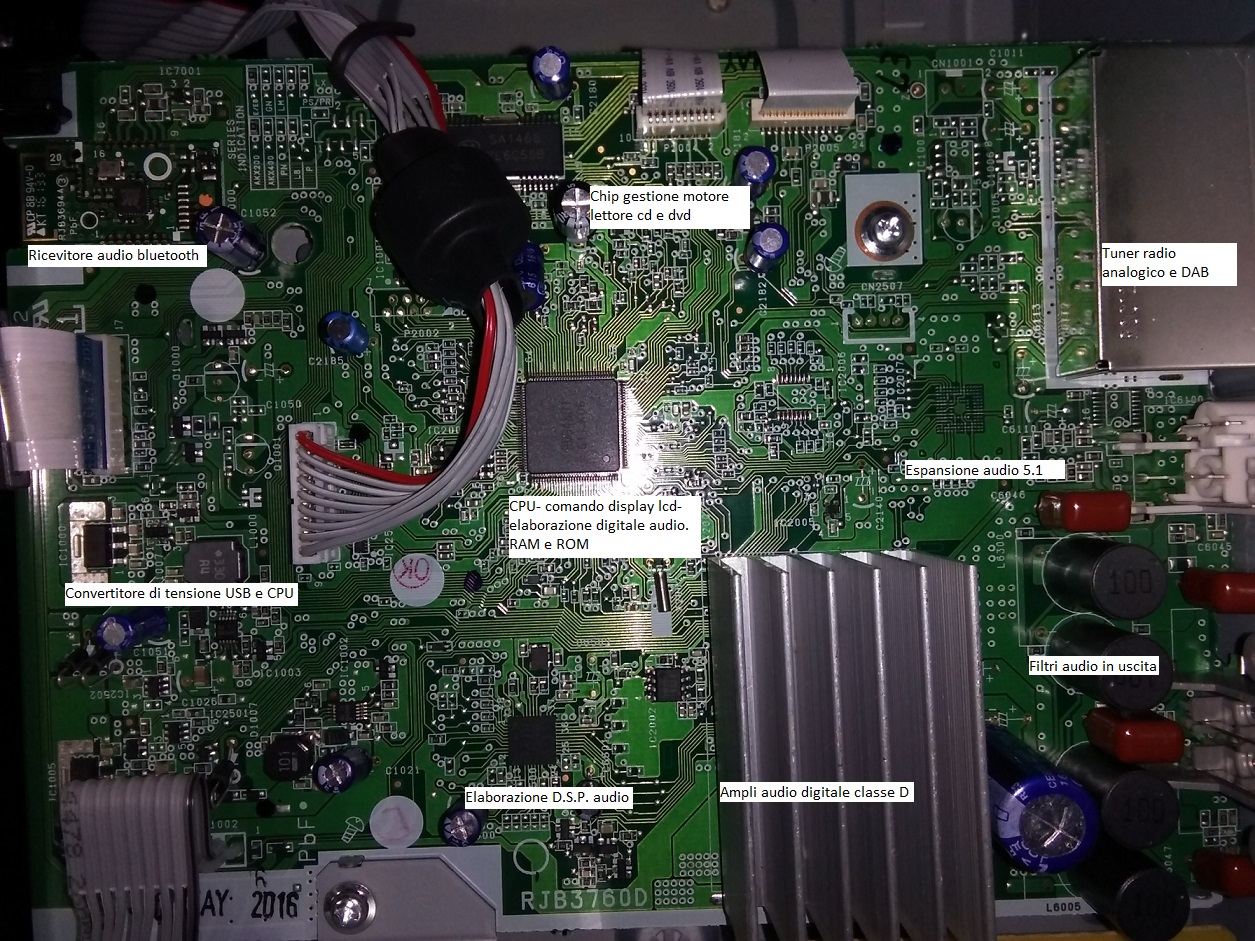
In practice, with the change of only the architecture management software and a few other hardware changes, the same circuit becomes a radio (with the addition of a radio frequency chip), a measuring instrument, a tablet, a smartphone, an LCD TV. , an LCD monitor, an MP3 player-recorder, a control unit for a combustion engine with both traditional and hybrid electronic injection and so on, adapting the management software and hardware according to the needs. In the following zoomable images you will find confirmations to what has just been explained.
Motherboard of a generic Tablet with indication of the mainboard components of a fully digitally managed mini Hi-FI
Of course I repeat that it is impossible to condense everything there is to say about IT in this text, but if you intend to deepen or need professional advice, you can contact me via the "Contacts" page.
Homepage The software Computer networks
Home
Informatics, Computer networks , Software and operative system
Electronics, Active components, Passive components
Radiotecnics
Seismology
Contacts
Who i am
Audio
Created and mantained by Armando Caligiuri (C) 2024 Version 3.2 ext
Armando Caligiuri, Electronic senior expert, Electronic and I.T. maintainer, electronic project implementer, I.T. consultant
Webmaster Armando Caligiuri, for the use of the contents of the site visit the Disclaimer page