 AArmando
Caligiuri electrons in motion
AArmando
Caligiuri electrons in motion

Welcome to the page dedicated to the computer networks
On this page you will find, exposed in simple words the history and current developments of computer networks, as already reiterated in the other pages it is impossible to condense in this small text everything there is to say on the subject, but if you need clarification or a professional advice you can contact me via the "contact" page.
You Find here on this line and at the bottom of the text the links to go to the "computer and hardware" page and to the page dealing with "software". We said on the "computer" page that computer systems have now become indispensable in all fields, due to their computing power and absolute versatility, given by being able to use specialized or more suitable software (or application) when needed.
But the real revolution began when it was realized that by networking the various machines, it would be possible to share data, peripherals and jobs. We then started to add network adapters to the PCs, then not really fast (1 Mbps) but suitable for the purpose, and to connect the PCs together creating the so-called local L.A.N. (local area network), using then archaic but effective network protocols for the purpose, such as the NetBEUI (NetBIOS Extended User Interface) or the IPX-SPX protocol.
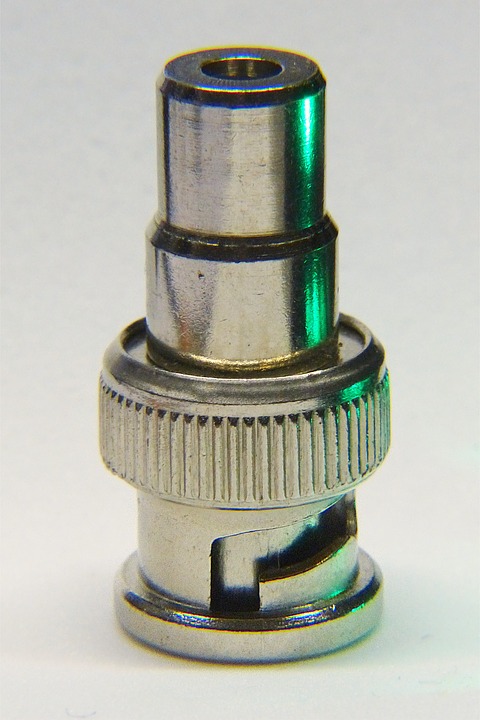
This type of networks could not overcome, due to intrinsic limits to the physical connection itself and to the protocols used, the speed of 10 Mbps, they were made with closed-loop technology (Token Ring) and used for the physical connection of the RG58 radiofrequency shielded coaxial cable. , with impedance (Z) 50Ω and terminated with BNC connector.
Topography of a Token ring network BNC connector used to terminate the RG58 cable
The subsequent arrival of a revolutionary network protocol, which TCP / IP was and is, has allowed for more reliability in the transmission of digital data, and to direct them with absolute certainty, this has imposed the study of a transmission line that allowed a much higher transfer speed than those used up to then, it was therefore decided to use the UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) cable, with twisted pairs, i.e. with four pairs of wires twisted two at a time, for which four pairs of wires, these cables have various quality categories, the one currently used for most networks is category 5e (extended).
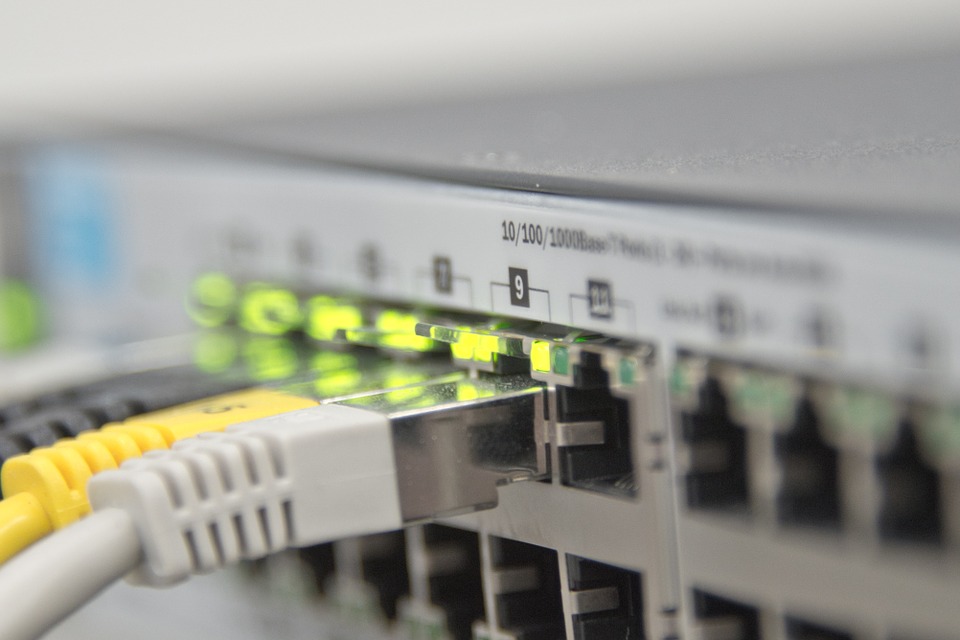
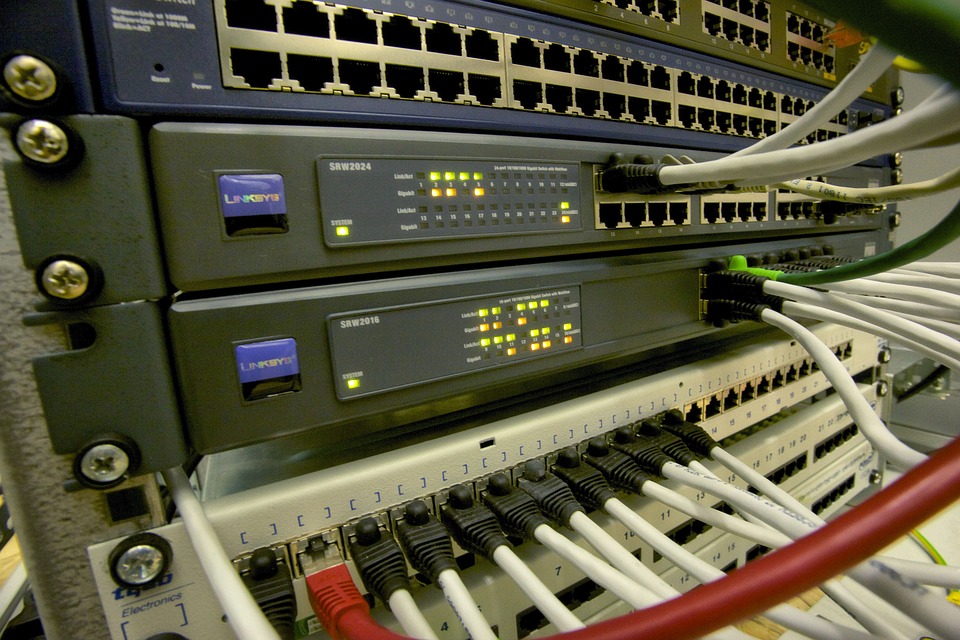
The networks using these cables, headed with appropriate eight-contact telephone connectors (RJ45), and with appropriately arranged wires, allow for data transmission speeds of up to 100 Mbps at a maximum distance of 100 meters, and for connections short, at most 10 meters, allow to reach a speed of 1000 Mbps (1 Gbps), for longer distances the STP cable (Shielded Twisted Pair) is used, almost the same as the UTP but with the shielding of both the single pairs and an enveloping one the totality of the pairs of intertwined threads. The cables are then connected to an electronic device called HUB (concentrator) or to its more intelligent relative, the SWITCH, usually placed in a cabinet placed in the center of the network itself, in order to keep the length of the cables as low as possible.
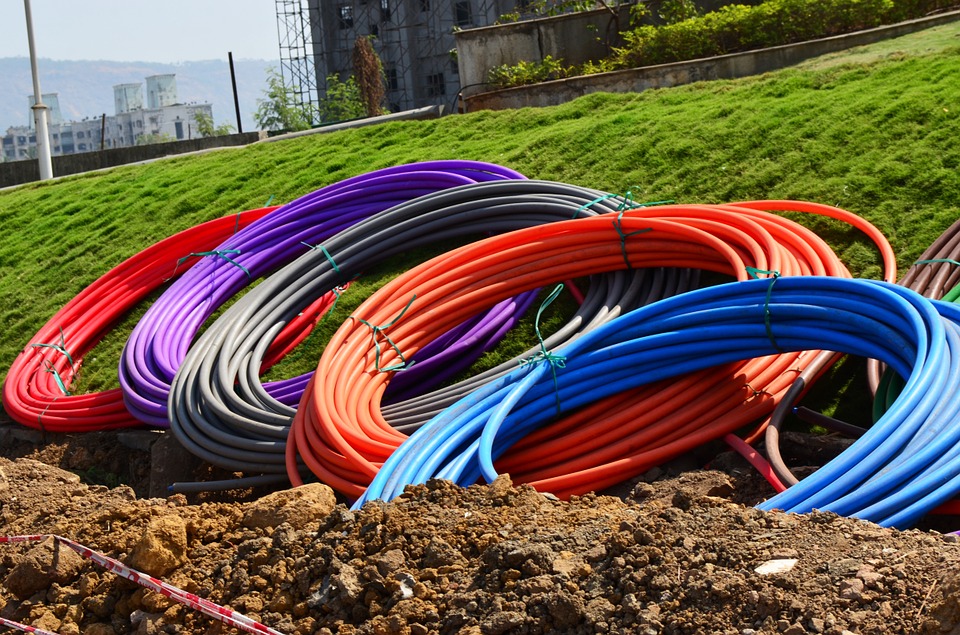
For higher speeds or for long
distances, the optical fiber
is used, which is made up of an internal light transmitting material
(filaments of plastic or glass material) and an external rubber coating,
the transmission medium is LASER light modulated by
digital impulses. It allows very high transmission speeds and almost
total immunity to disturbances, making it ideal for creating
M.A.N. (metropolitan area network) and
especially W.A.N. (wide area network).
The interface between LAN networks and M.A.N. and W.A.N. is made by means of an electronic device called ROUTER (router), which with the collaboration of a modem, which decodes the data flow coming from the telephone network, allows to route the data flow coming from the WAN network to the LAN network (and vice versa ) using NAT technology (network address translation), i.e. the connection of a certain number of IT devices (LAN, maximum 256 at a time) to a single network (WAN or MAN).
There are, are very widespread and tend to spread more and more also home and business networks made with wireless devices (Wireless)which use a radiofrequency carrier (band assigned by CEPT with frequency 2.4 GHz or recently the band a 5 GHz), modulated with digital technology to connect the IT equipment together, we therefore have wireless network adapters for PCs, wireless switches called access points and wireless routers that allow you to create the networks described above. They are in full development thanks to the opportunities they offer, such as being able to connect without laying any type of cable, being able to connect even outdoors, being able to create LAN networks in historic buildings without carrying out masonry work and are ideally used with small terminals such as smartphone or tablet of all kinds.
Like everything, even the
wireless network has its downside, considering the health risks involved
in having one or more transmitting devices at very short wavelength at
home, risks which, among other things, do not yet have. the effects are
known, the other main disadvantage cannot be overlooked, namely that the
transmission and reception speed is limited by the fact that it is a
half duplex communication (or transmission, or reception,
therefore not simultaneous), while the network wired is full
duplex (simultaneous transmission and reception of
information), another disadvantage is given by the limits imposed by the
medium itself, which being limited in power, for obvious reasons the
quality and consequently the speed will degrade very quickly with the
distance and the presence of radio interference.
At the moment the maximum speed is given by the 802.11AX-2021
MIMO standard with speeds of 10 Gbps (Half duplex), previously
there were the 802.11N at 150 and 300 Mbps, the 802.11G
at 54 Mbps and the 802.11B at 11 Mbps.


Wireless router with Diversity system USB-type wireless network adapter
The arrival of the largest WAN
network in the world, i.e. the
Internet, has then made it possible to connect billions
of computers and IT equipment located in every location in the world and
consequently the broad spectrum sharing of data, work, knowledge and
creation.
e-commerce, i.e. electronic commerce, a real revolution. To tell the
truth this has created and also creates some headaches, we talk about
computer viruses,
data theft, identity theft and computer crimes.
The
Internet network offers many
opportunities but you have to know how to use it wisely and carefully,
it is not a place for the naïve, or at least it shouldn't be, instead we
are currently witnessing the connection to the large network of various
machines (IOT) that have nothing to do with IT, ie washing machines,
kitchen machines, refrigerators, TVs, smartphones and more.
The Internet has also led to the explosion of social networks, such as
Facebook, whatsapp or Twitter, which allow you to
communicate at an intercontinental distance without leaving home.
Access to the Internet is guaranteed by large telephone operators, making it possible to access the wired network and the mobile network. Currently, the large mobile telephone operators have sniffed out the business opportunities associated with mobile wireless networks, to be combined with the wired one in the ISP business (internet service provider) and invest a lot in it with continuous innovations that increase its speed, we are talking about 4G or LTE which travels at speeds around 150 Mbps and previously 3G, which had already brought with it in its latest evolution (HSDPA +) a substantial increase in both speed and a decisive decrease in latency and PING (evaluation parameters and network quality tests), the new 5G technique is currently being implemented which will bring speed and latency to values unimaginable until now . The 5G network will be used for the decisive development of the internet of things (Internet of things abbreviated with I.O.T.) and for the autonomous driving of vehicles thanks to the very high speed, and the very low latency and PING.
However, the wired network is also undergoing a substantial evolution, with the fiber optic connection gradually reaching even the most remote places, guaranteeing a minimum speed of 20 Mbps.
Below is a series of zoomable images that will allow you to get to know more closely what we have talked about so far
STP network cables with shielded RJ45, connected to a switch Switch cabinet connected to the main patch panel, the red cable is the uplink
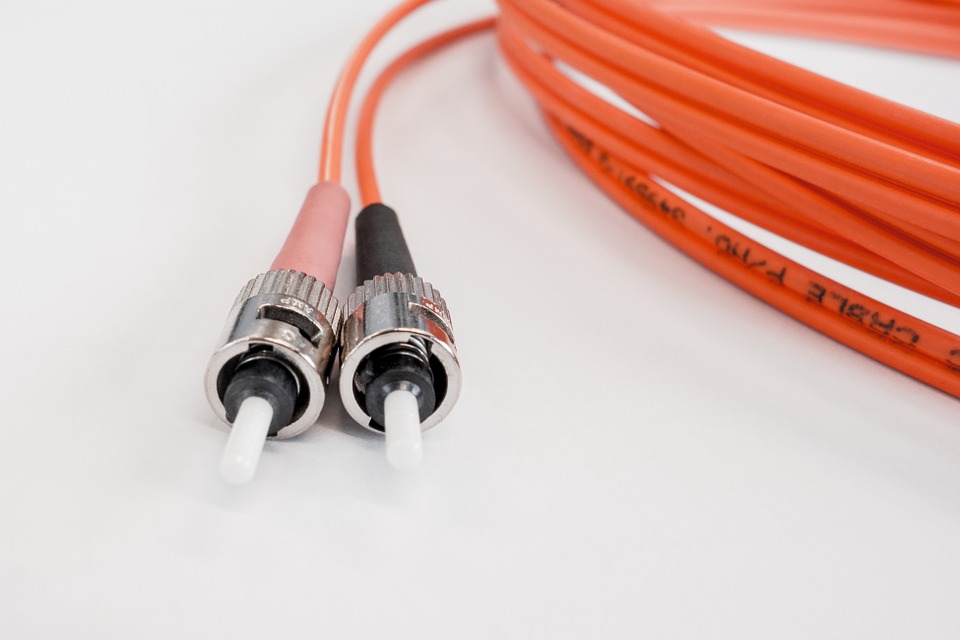
Fiber optic cables ready for underground laying for WAN network Connectors for connecting the optic fiber to the main network switch
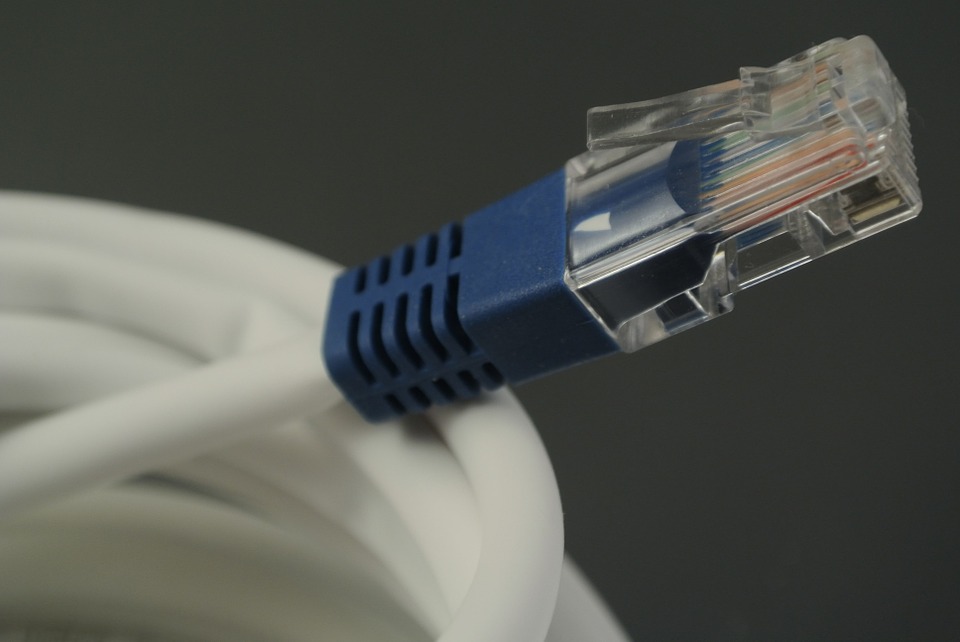
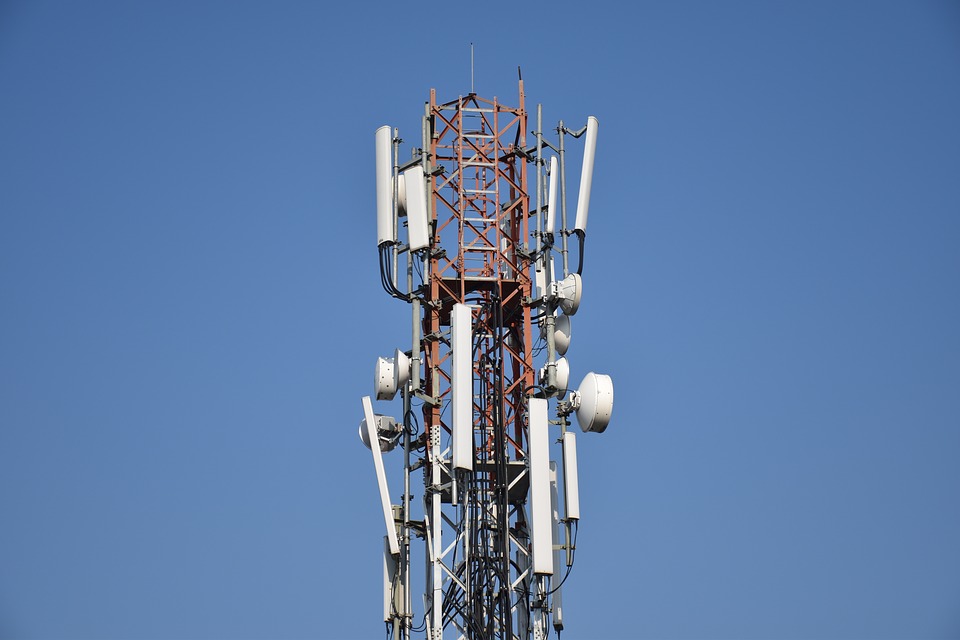
UTP network cable with RJ45 SRB tower with digital radio links and antenna system propagating 4G and 5G
I repeat again that it is impossible to condense in these few lines everything there is to say about the subject under discussion, so if you want to learn more or need professional advice you can contact me by going to the "contacts" page of this site. I hope that what has been created is to your liking, good navigation
Homepage The software Informatics and hardware
ss
Home
Informatics, Computer networks , Software and operative system
Electronics, Active components, Passive components
Radiotecnics
Seismology
Contacts
Who i am
Audio
Created and mantained by Armando Caligiuri (C) 2024 Version 3.2 ext
Armando Caligiuri, Electronic senior expert, Electronic and I.T. maintainer, electronic project implementer, I.T. consultant
Webmaster Armando Caligiuri, for the use of the contents of the site visit the Disclaimer page