 Italiano-
English-
日本語
Italiano-
English-
日本語
Welcome
to my web page dedicated to active electronic components
On this page I will try to define with words
suitable for everyone the immense world behind the simple phrase
"electronic active components" is not an easy task but I will try. Of
course, as already mentioned on the other pages, it is impossible to
condense a vast subject in this small text, but if you intend to
investigate further or you need professional advice, you can contact me
via the Contacts page.
Active electronics
components
While the
passive components
had only dimensional and qualitative evolution, on the contrary the
active components have known over time real earthquakes in their
evolution, with entire systems and production concepts disappeared,
replaced by other revolutionary systems and production concepts, we
moved from thermionic (or vacuum) components to
solid-state systems
around 1960, which started the revolution that allowed us to achieve
everything we see now (smartphones, LCD TVs, personal computers,
tablets).
Now let's get to know the main active
components, they are transformers,
thermoionic tubes (also called
valves),
transistors
and
integrated circuits.
The
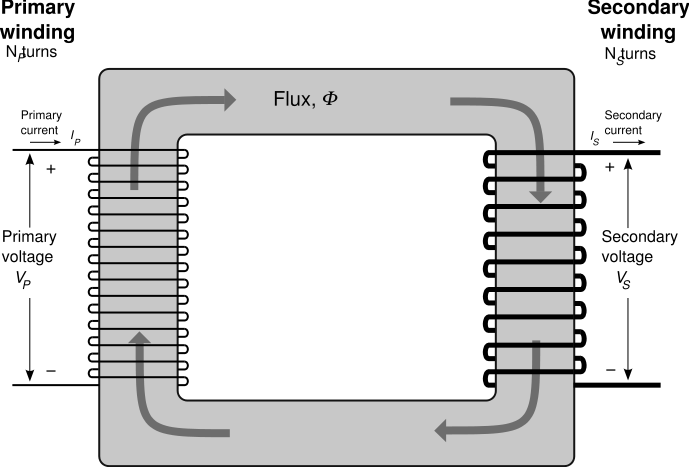
electrical transformers are defined as "active
machines without moving parts" they are formed by two coils of copper
wires mounted on a pack of laminations and separated by a core (see
images at the end of the discussion) the coils are called a "primary" el
'other "secondary" depending on the direction of operation. Transformers
allow through the law of electromagnetic induction (Faraday-Neumann-Lenz
law) of transferring lowering or raising the value
(transformation ratio), tensions and electric currents, they also ensure
the physical separation between circuits, since there is no contact
between the primary and secondary, and act also from impedance adapters
in professional audio equipment. The size of a transformer depends on
the current and the voltage it must manage, the working voltage and
current values are usually printed directly on the transformer itself.
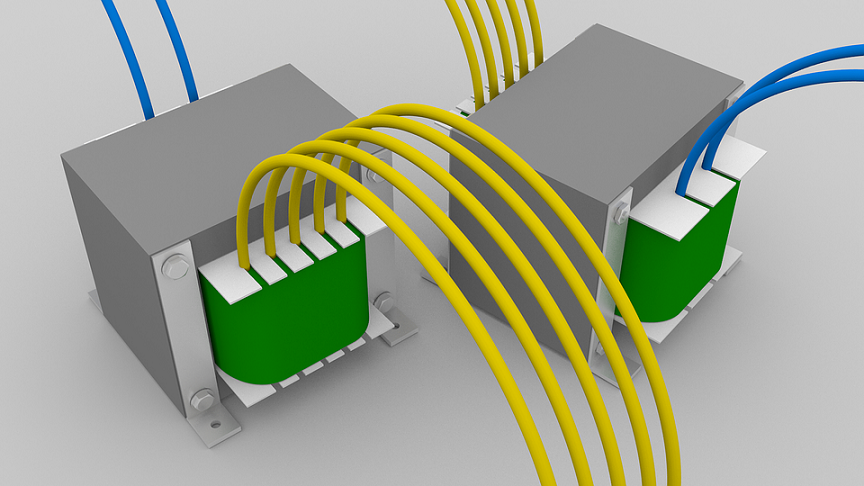

Low tension transformer
Electrical symbol of the transformer
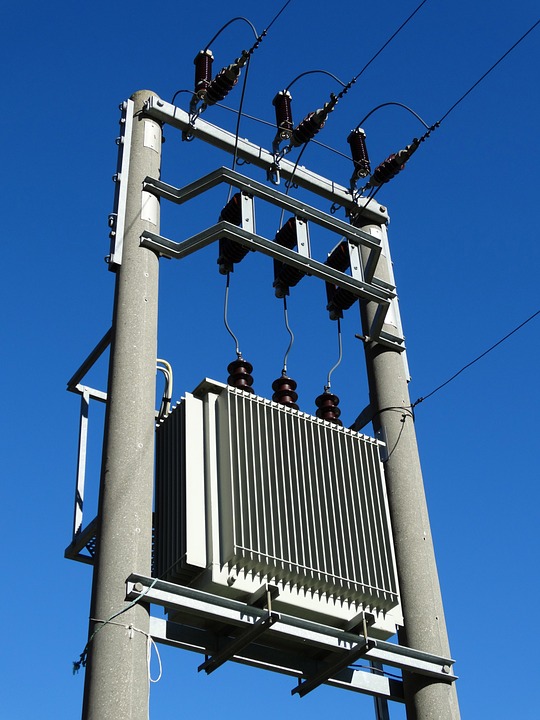

Pole high voltage
three-phase transformer
Operating principle
Thermoionic tubes or electronic valves were the first active
components to allow the amplification and processing of electronic
signals, TVs, radios, transmitters, and even computers (of gigantic
size) were made with them.
They exploit the thermoionic effect, which consists in the emission of
electrons in the vacuum, by an electrode called "cathode", with negative
polarity, made with a particular material, which is heated by an
incandescent tungsten filament, the electrons emitted moving in a
vacuum, they have no particular obstacle and are attracted and collected
by another polarized electrode, positively called an anode or plate,
this is the thermionic diode, a component (also available in solid
state) that gets crossed by the current in a single sense (direct
polarization) and not in the other (reverse polarization).
If we now add a third electrode called grid between anode and cathode,
and polarize it slightly negative, we will be able to control and
modulate the flow of electrons moving in a vacuum, in other words by
applying a small signal to the grid we will get a signal much wider on
the anode, we have thus realized a
triode, the simplest thermoionic device, and also the first one
realized able to amplify an electric signal, the electrodes are enclosed
in a glass ampoule in which the vacuum has been obtained. If you need
more information, you can go to the
contact page.
Multi-grid tubes have been manufactured to satisfy particular needs,
tetrodes (two grids), pentodes (three grids) and tubes having in the
ampoule not the vacuum but a rarefied gas.
Although replaced in almost all applications by solid-state devices,
they continue to be irreplaceable in some devices, such as in high-power
high-frequency amplifiers, hi-fi applications for the particular and
pure sound that they can produce, even in the oven There is a high-power
valve in the microwave that we all have at home to produce the very
short-term emissions that cook food. And the cathode ray tube that until
a few years ago allowed us to see some splendid images on CRT TV was a
valve with the screen acting as an anode.
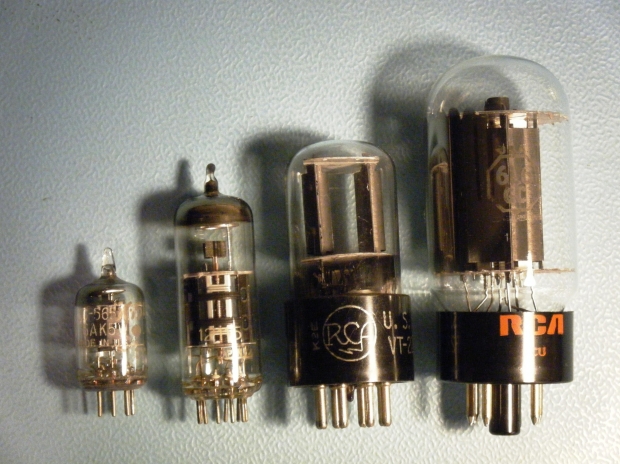

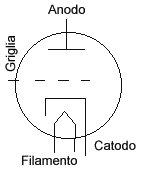
Thermoionic tubes for
radio applications Electrical symbol of the vacuum triode
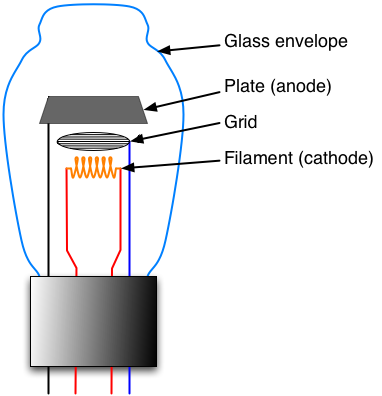
Working
principle of the triode
Semiconductor or solid state devices
Particular active electronic components are constructed by doping (by
introducing impurities) suitably a semiconductor material (germanium,
silicon or artificial semiconductors), the semiconductors are doped with
P-type impurities with positive charge (gap or lack of electron) or
N-type with negative charge (excess of electrons), the contact between a
charge P semiconductor with another with charge
N produces a
P-N type
junction, in the contact zone a current called depletion is created due
to the exchange of charges in the attempt to restore the neutrality of
the materials, thus creating a neutral zone near the contact and a small
insulating layer to the contact itself. It should be noted that the
P-N
junction subjected to direct sunlight is able to produce an electrical
voltage of 0.6V (photovoltaic effect) in the contact zone, therefore it becomes a
photovoltaic-effect solar cell, appropriately arranging many junctions
(series and parallel) yes they get the photovoltaic panels currently
used in production plants. If you need more information, you can go to
the contact page.
Using the properties of the PN junction it is possible to obtain all the
components that are the basis of modern electronics, including
solid-state diodes, TRANSISTOR, MOSFET,
JFET,
UJT, these components can be made either in discrete form, ie
as a single component with certain characteristics, or as an integrated
circuit, or a semiconductor crystal that duly appropriately, allows to
obtain a complete circuit of passive and active components in very
little space and with great material and time savings, but let's get to
know more from near the various types of semiconductor components.
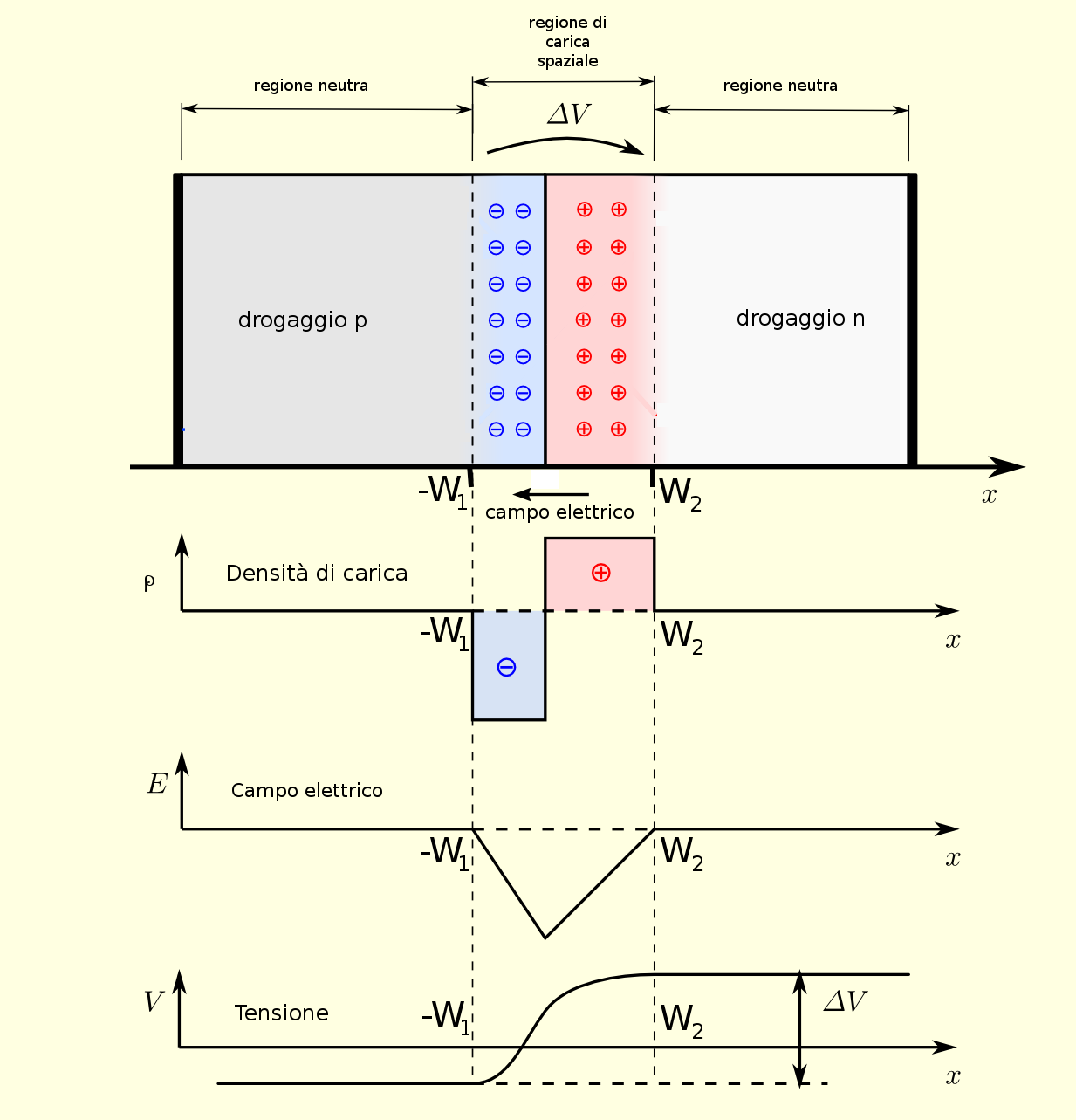

Graphic illustration of the P-N junction
Photovoltaic cell multiple P-N junction
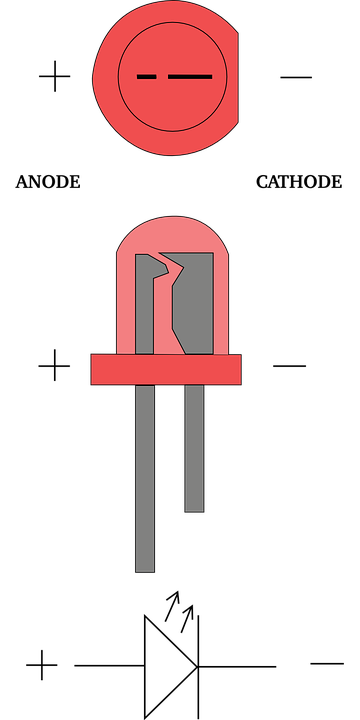
The
semiconductor
diode uses a single
P-N junction, due to its known properties, it is able to be
crossed by current or not depending on how we apply voltage to it. It
has two external connections, one being connected to the doped P
semiconductor (anode),
the other to that N (cathode), if we apply
the voltage with the positive pole to the anode and the negative one to
the cathode the diode will be crossed by the current (direct
polarization), if instead we invert the poles the current will not be
able to cross the diode (reverse polarization), they are used as
rectifiers in power supplies, as switches, as detectors and as
protection (combined with a fuse) against power supply polarity
reversals.
Keep in mind that the diodes have a threshold
voltage of 0.6V for those with silicon and 0.2V for those with
germanium, ie if the voltage across them does not exceed this value they
behave like an open switch (no current flows ), silicon diodes with
lower threshold (Schottky diode), diodes are used which
are used as variable capacitors (varicap diode) by
varying the voltage at their ends and particular voltage stabilizing
diodes called Zener
diodes.
It is impossible then not to mention the
L.E.D. (light emitter diode), special diodes
that emit light from the PN junction, then amplified by a special lens,
they are revolutionizing the field of lighting thanks to the very low
current consumption and the particular light that they can produce, from
simple indicators they they have evolved with the increase of the light
emitted and with the obtainment of white light, lamps of all types and
colors are currently manufactured, and also provide the backlight for
the LCD screens (edge LEDs) of the latest generation TVs.
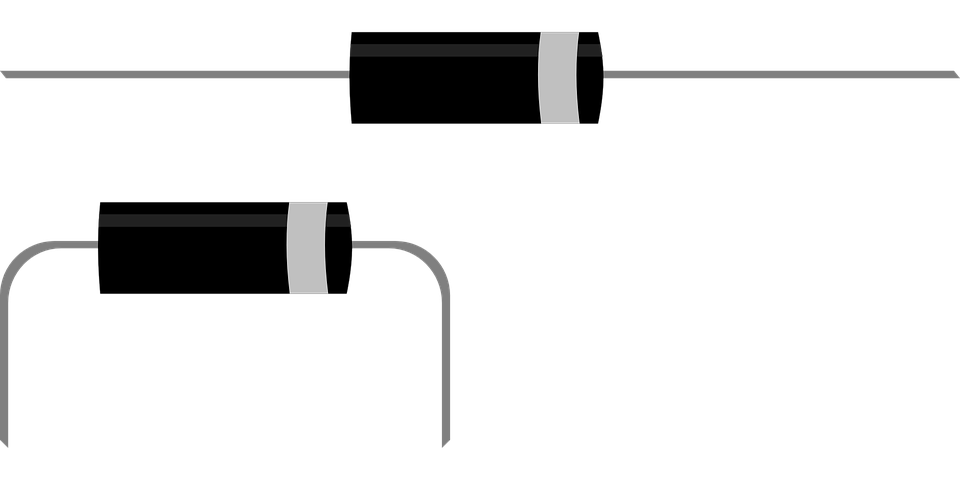
Real diode, the white band is the cathode
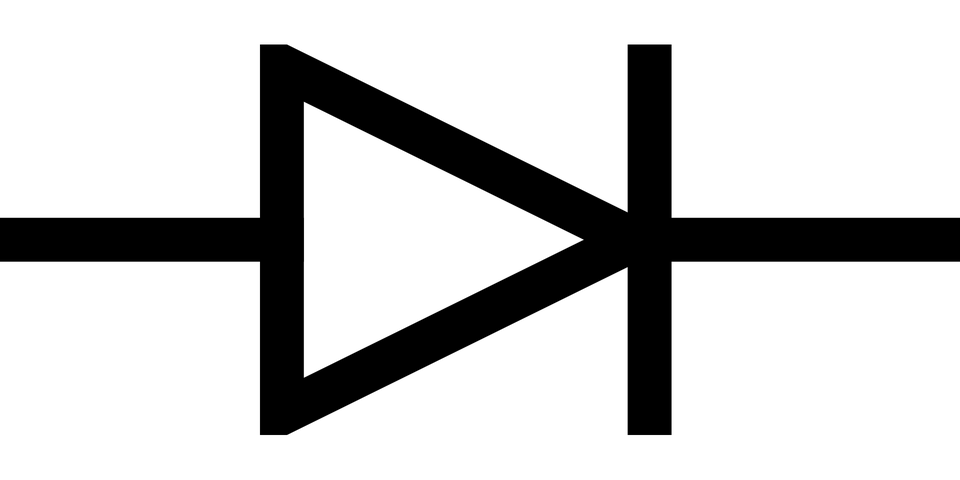
Electrical symbol of the diode
LEDs of various colors Internal scheme and symbol of the LED diode
If you need more information or professional
advice, you can go to the
contact page.
The bipolar or
BJT
transistor is a component
formed by two PN junctions (see figure below), it can be of the
PNP type or of the NPN type, and it has three
terminals called, Base
(or Gate), Collector, Emitter (indicated in the electric
symbol by an arrow) .
It was discovered in
1946 in the Bell
telephone labs by researchers Walter Brattain, John Bardeen and William
Schockley, they started modern electronics.
The transistor is an active component capable
of amplifying the signals applied to it, such as the thermionic triode,
but with many advantages, the main ones being that of being a solid
state and therefore difficult to destroy mechanically, it is small if
compared to tubes, it works with low voltages at the ends and its
integration is relatively easy, moreover it does not require filament
tension.
Very schematically, its operation can be
defined thus, "the electrons emitted by the emitter, are regulated by
the base and then collected by the collector".
They are used as amplifiers, switches,
oscillators, regulators (combined with a Zener diode) and many other
applications.
With the progress of the solid state
component technique, other transistors optimized for some applications
have been introduced, including the JFET (high input
impedance), the MOSFET (switch with low resistance of
the channel when directly polarized) and the UJT or
unijunction (pulsed oscillator).
The transistors are enclosed in metal or
plastic containers depending on the required power dissipation and the
possible application of a heat sink.
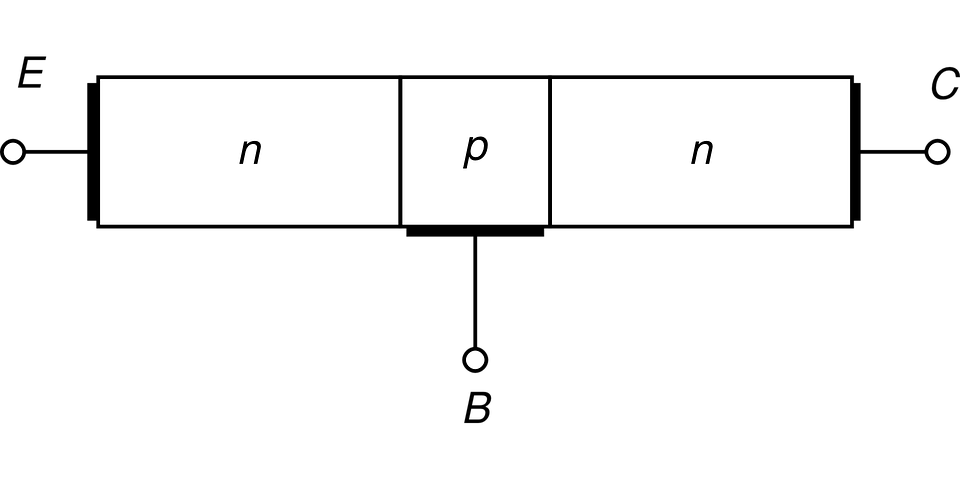
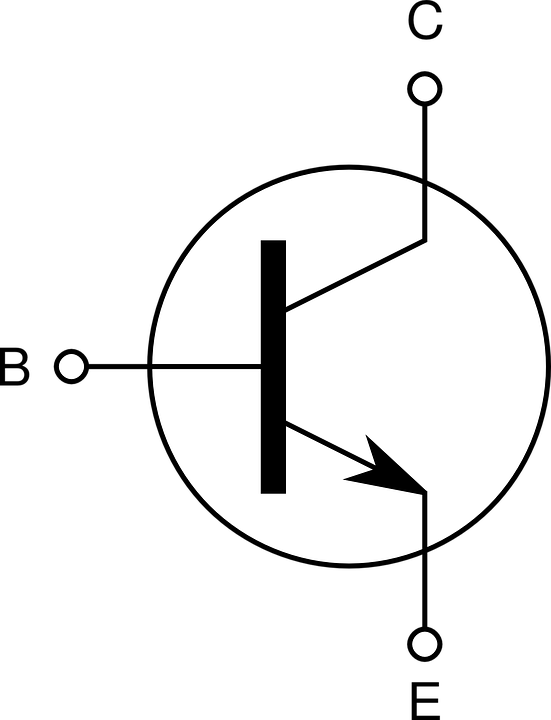
Internal scheme of BJT NPN transistor
Symbol of the BJT NPN transistor
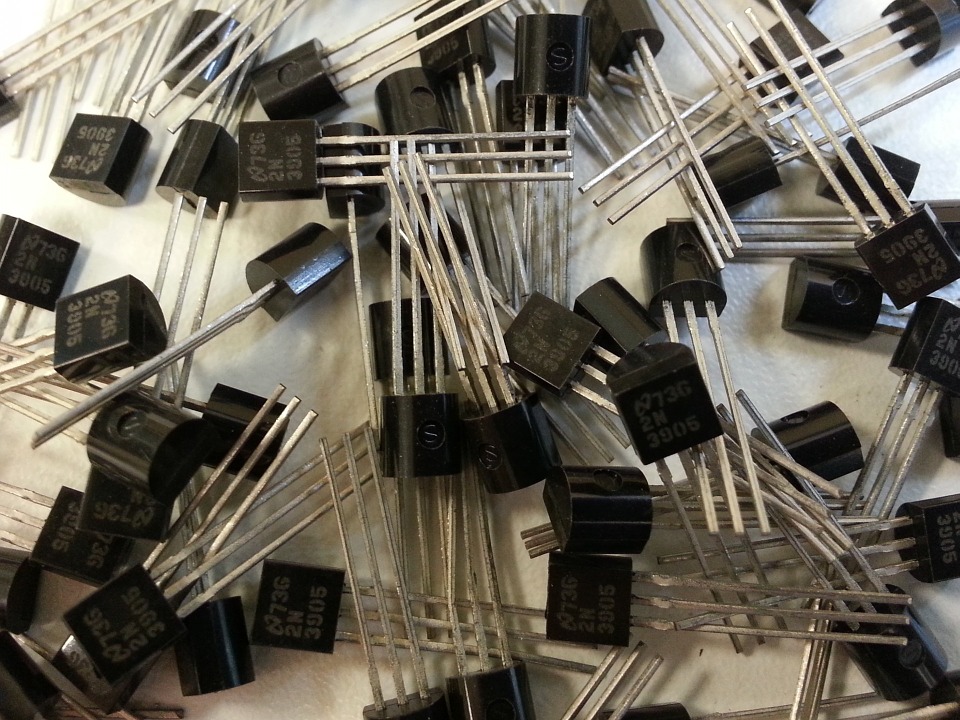

Power transistor with case TO220
Transistor for small signals in TO92 case
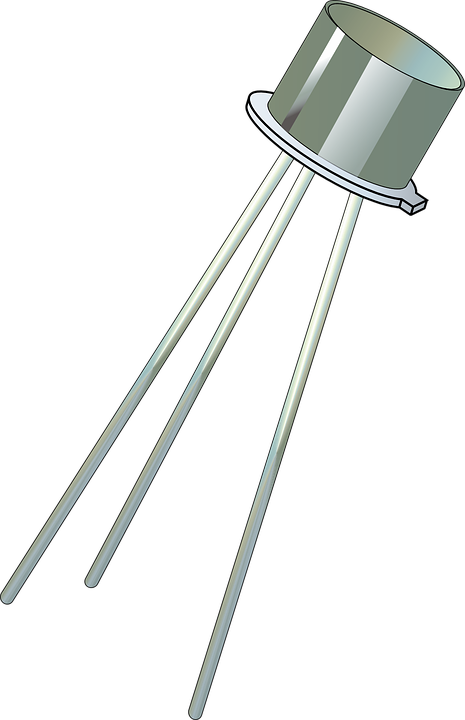


Transistor inTO18 case
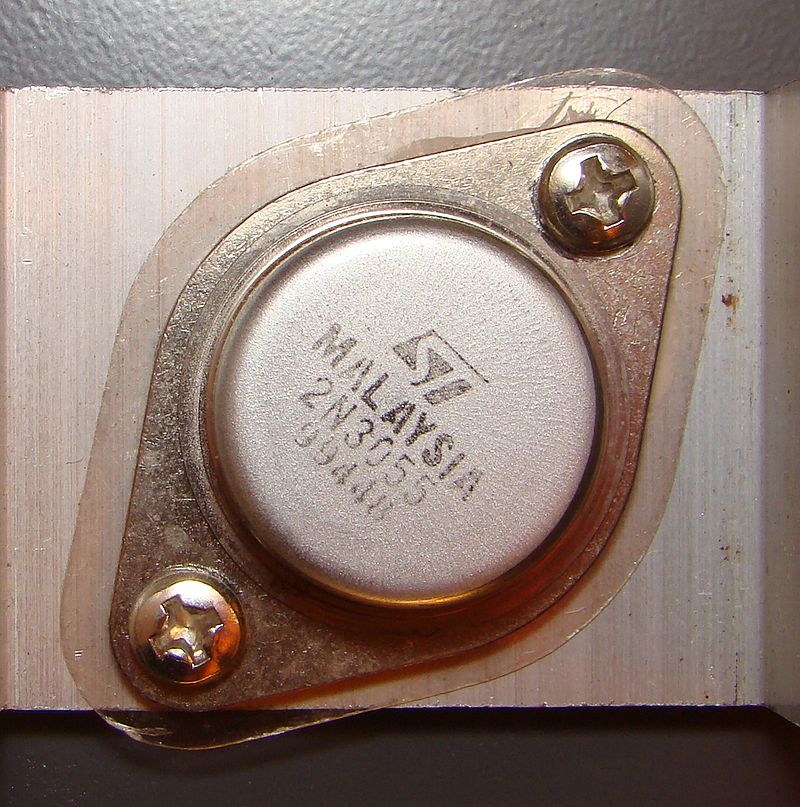
2N3055 metallic power transistor in TO3 case
Finally, the
monolithic
integrated circuits are made by
doping the areas of a semiconductor chip in a suitable way, in detail,
by introducing more or less conductive impurities insulators or
conductors (or resistors of the desired value) will be realized, P or N
type impurities will realize transistors with the desired
characteristics, by doing so you will obtain on a small semiconductor
chip a complex circuit, accessible from the outside with terminals so as
to be able to connect to the outside the components necessary for
operation but not integrable (inductances, capacitors, resistors and
other ).
There are analog and digital integrated circuits that perform very
complex functions, it is thanks to them that electronic circuits have
been miniaturized, with visible results by all, just think of tablets or
smartphones, real miracles of electronic technology.
Integrated circuits built with normal components, without a container,
are also produced, then enclosed in plastic containers and performing
functions that are in any case simple, these types of components are
called "hybrid integrated circuits". The STK series
hybrid amplifiers are a very common example.
To know the characteristics of the active components, you must be in
possession of the related datasheet.
The datasheets are information sheets, released by the manufacturer
where it is possible to find all the information regarding the maximum
and minimum parameters of the components' functioning, and even examples
of realizations, an excellent site where to find datasheets of almost
all the components can be found at
this link .
Instead clicking with the mouse
on this link you can
view by way of example the datasheet of a known component on the breach for many
years, the strange low frequency amplifier
TDA2003,
capable of producing a dozen Watts, using few external components, you
will also find in the datasheet the internal diagram of the component,
and the examples of construction.
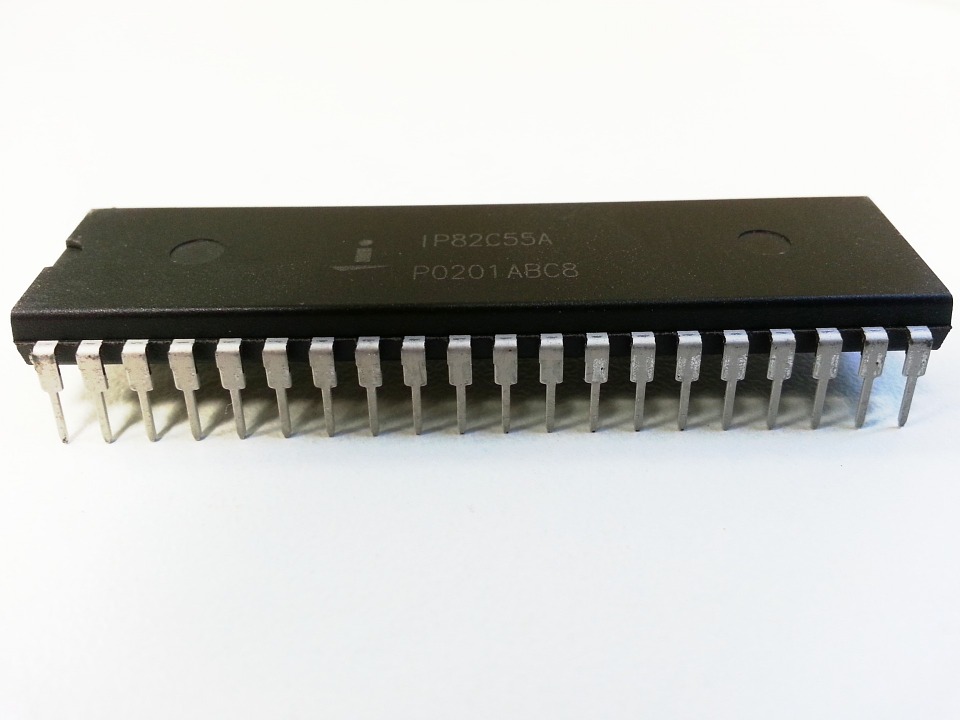

Integrated
circuit in D.I.P. case SMD
integrated dual in line
(DIL)
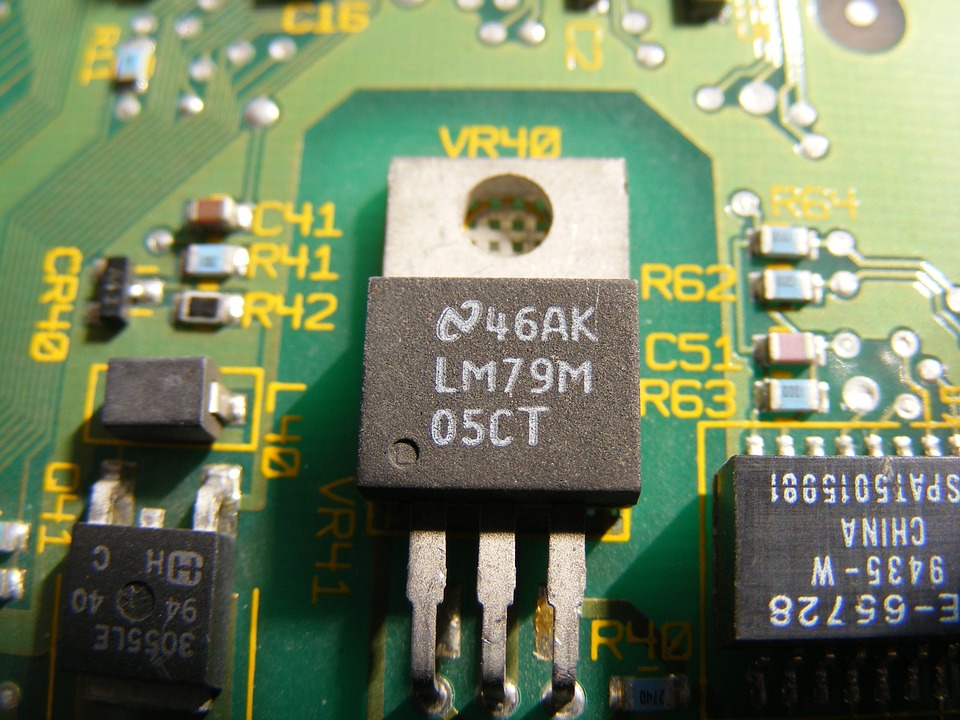

Integrated circuit 5V negative regulator
Integrated circuit SMD flatpack
Of course it is impossible to condense all these concepts in a small
space, mine wants to be only a good guide for those who look out on this
fantastic world, it is possible however to deepen or request a
professional consultation by contacting me, for this go to the
contact page.
Thank you for visiting my website and following my guide, come back to
visit it.
Informatics, Software and O.S., Computer network
Electronics, Active components, passive components
Radiowave
Seismo
Contacts
Who I am
Sitemap
Audio
Terms of use
Armando Caligiuri, Electronic senior expert, electronic and I.T. maintainer, I.T. consultant
Web master Armando Caligiuri
(C) 2024 V3.2